Karst landscapes above ground display characteristic features formed by the dissolution process. These features range in scale from small surface details to extensive landforms.
Karren:
The term karren encompasses all small karst features on rock surfaces. They form in:
- Bare Karst: Exposed rock with inclined surfaces and sharp ridges.
- Covered Karst: Rock covered with a layer of soil, so the dissolution process is more evenly distributed, resulting in softer, rounded features.
Depending on the properties of the rock and the inclination of the surface, different types of karren are created. Here are a few examples of different types of karren:
- Roundkarren (covered karst): Winding, rounded furrows created by solution weathering in soil enriched with CO₂ from organic material. After the soil layer has been removed, these structures become exposed – you can see an example here at this station of the Geo.Trail.
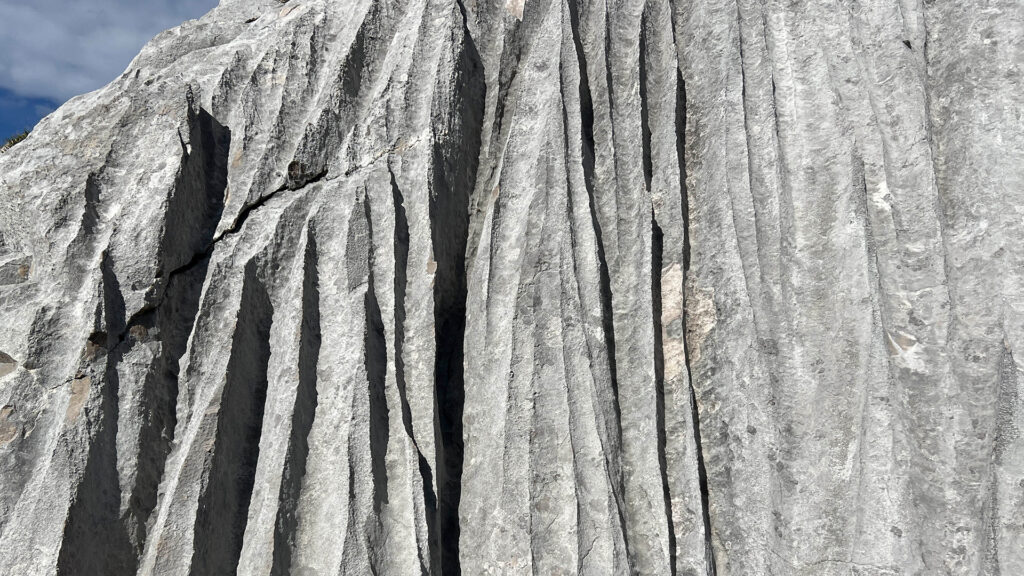
- Rillenkarren (bare karst): Parallel, narrow grooves form on exposed rock as acid rainwater erodes the limestone. You can discover such karst structures above the tree line in the Rofan Mountains.

Bare karst forms on exposed and inclined rock surfaces. As rainwater absorbs CO₂ from the atmosphere, it becomes slightly acidic and dissolves the calcareous rock. This process creates sharp-edged rillenkarren, where water flows parallel to the slope. In contrast, when limestone is covered by soil, the water absorbs additional CO₂ from the organic matter, leading to the formation of roundkarren with smooth, rounded shapes. (Image source: Own illustration)
Large-scale surface shapes
Not only small-scale forms such as karren, but also large-scale landscapes are formed by karstification. Examples are:
- Sinkholes: funnel-shaped depressions resulting from cavity collapse
- Uvalas: Linked sinkholes forming larger depressions
- Poljen: Expansive, flat karst basin
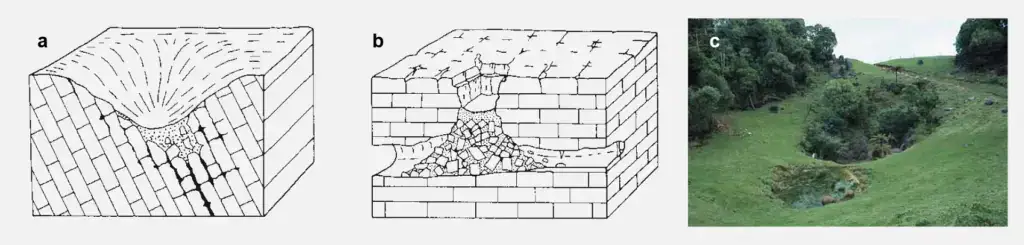
Dolines are large-scale surface forms that are created by karstification. There are different types of sinkholes. a) solution doline, b) collapse doline; c) Here you can see two small sinkholes on the North Island of New Zealand. (Image source: Ahnert 2009, Fig.: 23.3 and 23.4, Chapter 23 Karst Formen, pp. 287-288)

